Examples of Information Design/ Instruction design
Power-point presentations – PowerPoint’s are designed to provide an informative yet visually pleasing presentation. A PowerPoint consists of a series of chosen images and information created for artistic and informative purposes.
Podcasting/ Instructional – Podcasting is a form of RSS feed technology represented through visual images portrayed with information aided through audio technology. Example would be Podomatic (http://www.podomatic.com) a website designed for users to able to upload and share your podcasts.
WordPress/ Blog spot – An open publishing application designed for blogging purposes. WordPress is designed to allow users the ability to provide informative as well as aesthetically pleasing information, for other users.
Online Kiosk’s – Online Kiosk’s for financial bank institutes such as Commonwealth Bank and St George are examples of instructional design. These websites are designed to allow users the ability to access banking information etc from the comfort of their own home.
Brochures – Referred to also as a pamphlet or note booklet, is usually designed to provide summarised or introductory information such as written text and pictures. Brochures inform the designed target market
Instructional Design Examples:
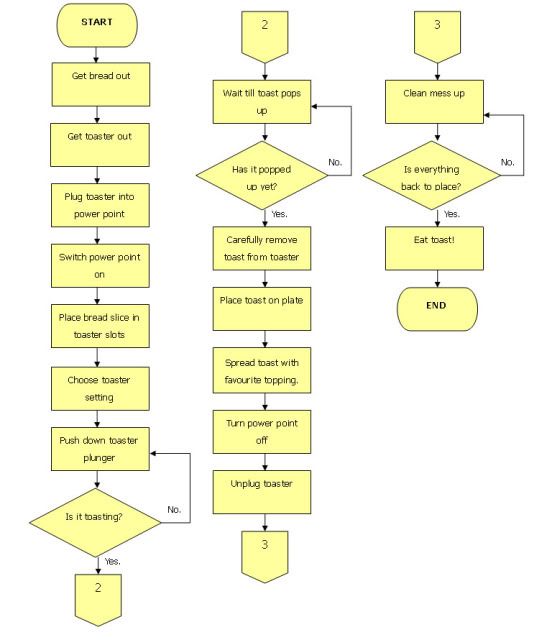
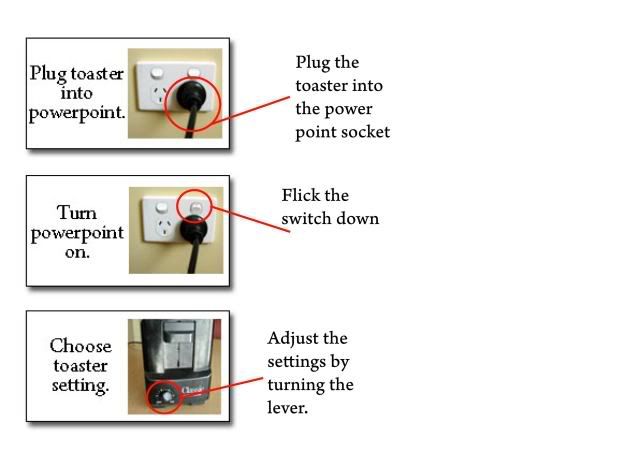
Manuals – A manual is another form of a booklet. Manual is essentially designed entirely for the purpose to inform as well as instruct the user on how to operate a particular designed function.
Instructional/ Interactive multimedia – Companies which design educational based interactive multimedia are also a form of instructional design. The learning company, provide a selection of instructional designed software, aimed at educating young minds. (http://www.learningcompany.com)
Online Video Media – Websites such as ‘Expert Village’ provide numerous instructional or “how-to-do” videos which are designed to educate the user without having the leave the comfort of their own home. (http://www.expertvillage.com)